Cultivating Social Resilience: Exploring the Intersection of Vertical Farming and Urban Sustainability
Vertical Farming and Sustainable Urban Agriculture
In this current world, full of urbanization, the combination of a quickly growing urban population, shrinking arable land, and the looming threat of climate change poses an urgent challenge, which is; how do we sustainably feed cities? As traditional agricultural practices struggle to keep up with the demands of urban centers, urban populations are increasing while arable land decreases. The urgent question of how to sustainably feed our cities arises against the backdrop of climate change with this. With these dramatic shifts in population and practices in agriculture, innovative solutions are important to ensure food security and environmental resilience. A revolutionary approach that reimagines in agriculture is vertical farming. By using the latest technology and design resources, vertical farming offers the potential to turn skyscrapers into thriving hubs of food production. This idea of transformation not only addresses urban food shortages but also helps to protect our environment from harm.
Vertical farming integrates cutting-edge agricultural techniques with sustainable urban planning, creating self-sufficient food production systems that reduce reliance on traditional farming methods and long-distance transportation of food. By utilizing often unused urban spaces such as rooftops and abandoned buildings, vertical farming maximizes land efficiency and minimizes the carbon footprint associated with food production and distribution. Moreover, new vertical farms can cater to the tastes of city dwellers all year round, bringing fresh, healthy food no matter the season which also alleviates the issue that many urban places face, food deserts.
In contemporary discourse, vertical farming has emerged as a solution to address pressing global challenges such as food insecurity, environmental degradation, and urbanization. By leveraging agricultural practices, technology, and sustainable urban planning, vertical farming aims to revolutionize food production systems, particularly in densely populated urban areas. This is a topic of lively debate between researchers and environmental scientists, with industry perspectives and case studies to provide a comprehensive understanding of its implications and potential.
Industry Perspectives on Vertical Farming
In Forbes’ article “Supermarkets and Shoppers Must Embrace Vertical Farming, Our Future Depends On It,” Vonnie Estes and Phil Lempert offer industry perspectives on the challenges and opportunities of vertical farming.
Estes, the Vice President of the International Fresh Produce Association, wrote in the article about the need for collaboration between vertical farms and traditional agriculture. Estes highlights the importance of bridging the gap between different farming methods, articulating that, “the vertical farming industry does have a lot of promise and opportunity because grocery retailers want this product, want a surety of supply, want consistency of quality”, which underscores the growing demand for vertical farming products within the industry. Vonnie Estes emphasizes the importance of collaboration between vertical farms and traditional agriculture to address common goals and challenges. One example of successful collaboration is the partnership between AeroFarms, a leading vertical farming company, and the New Jersey Agricultural Experiment Station (NJAES). AeroFarms collaborated with NJAES to research and develop new varieties of leafy greens optimized for vertical farming environments. This collaboration not only improved crop yields and quality but also helped both the vertical farming experts and traditional agricultural researchers to understand each field and their respective pros and cons.
On the other hand, Lempert, one of America’s leading food and consumer trend-watchers and analysts, analyzes the role of vertical farming in overcoming the impacts of climate change on food security. He explains vertical farming as a revolutionary solution tailored to the needs of an increasingly urbanized world such as ours. Lempert states that “Vertical farming has become a revolutionary solution to the growing challenges of traditional agriculture in a world where climate change is raging havoc over growing our foods”, highlighting the urgency of embracing solutions like vertical farming to adapt to changing environmental conditions and ensure food security for future generations. Integration of vertical farming into urban resilience strategies is one example where vertical farming has demonstrated its potential. For instance, in cities prone to extreme weather events like hurricanes or droughts, vertical farms are resilient food production systems less susceptible to climate-related issues. Initiating vertical farming in regions experiencing water scarcity due to climate change is another example where vertical farming has demonstrated its potential. Vertical farming systems, such as hydroponics or aeroponics, use significantly less water compared to traditional soil-based agriculture. Regions like the Middle East have established vertical farms powered by desalinated seawater to produce fresh produce sustainably despite limited freshwater resources.
Recognizing the importance of teamwork and fresh ideas, professionals in the industry like Estes and Lempert are clearing the path for more people to embrace vertical farming. As this method gains popularity in the fight against global food shortages, it’s crucial to listen to the advice of those who know the industry best.
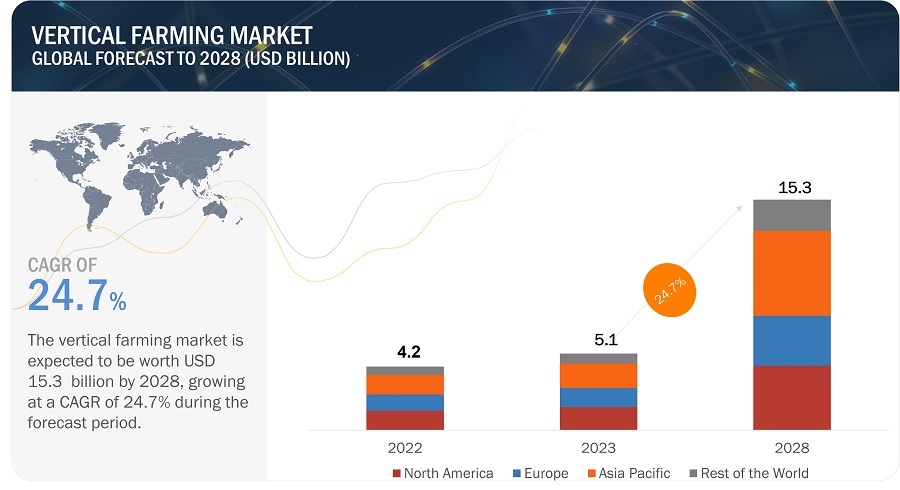
This is a graph showing the expected vertical faming market by the year 2018 with a breakdown of the top producers growth rate.
With long-term agricultural practices, compounded by pollution, contributing significantly to the depletion of natural resources, the need for advanced technologies in agriculture increases more day by day. The case study about the future of technology and food systems underscores the pressing challenges posed by resource scarcity, particularly in urban environments like Singapore. Traditional agricultural methods have historically strained land and water resources while intensifying issues such as land degradation and water scarcity. In response, Singapore has utilized hydroponics and aeroponics to mitigate these challenges. By reducing reliance on conventional farming practices that deplete soil fertility and consume excessive water, vertical farming offers a sustainable alternative to the traditional agriculture many nations continue to practice today. With the technology of vertical farming in our grasp, we can collectively “overcome the limitations imposed by conventional agriculture, thereby enhancing food security and environmental sustainability in resource-scarce urban settings”, according to the case study in Singapore. Additionally, the adoption of vertical farming technologies minimizes pollution risks associated with chemical fertilizers and pesticides, preserving water quality and supporting ecosystem health.
Scholarly Perspectives on Vertical Farming
Vertical farming offers innovative solutions to address pressing global challenges such as food insecurity, environmental degradation, and urbanization. Besthorn is currently a professor at the school of social work at Wichita State University and has various publications in the realm of social work and sustainable social action. Besthorn contextualizes vertical farming within broader discussions of environmental sustainability and social justice while underscoring the importance of collaboration in addressing societal challenges. He emphasizes the evolving nature of social work, stating, “Social work has never been singularly involved simply in the assessment, intervention, and treatment of individual psychological conditions.” This highlights the role of social work in initiatives like vertical farming therefore addressing systemic issues such as food insecurity and environmental degradation.
Similarly, Sanjuan-Delmás, a researcher and project manager with a masters in Environmental Studies with a specialization in Industrial Ecology, and his team of researchers’ study on the environmental assessment of integrated rooftop greenhouses (i-RTGs) underscores the innovative nature of vertical farming systems. Through an analysis of the environmental impacts of food production in urban settings, Delmás’ study demonstrates the environmental benefits of i-RTGs, emphasizing their feasibility in environmental sustainability. The authors explain that by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and optimizing resource usage, vertical farming systems like i-RTGs have the potential to enhance food security while minimizing environmental degradation. “Vertical farming,” they write, “is emerging as an effective measure to grow food in buildings and can increase food production in urban areas in a more sustainable manner”, further highlighting the potential of vertical farming in promoting sustainable urban agriculture. Building on the findings of Sanjuan-Delmás and his team’s research, a case study from Singapore researching environmentally future food systems further explains the potential of vertical farming in addressing urban food security challenges.
Yong Xing Tan, a researcher who is involved in the Advanced Environmental Biotechnology Centre and the Nanyang Environment and Water Research Institute, and their band of researchers sheds further light on the potential of vertical farming in addressing food security challenges in urban environments. Their case study highlights Singapore’s efforts to leverage technological innovations to enhance food security in a resource-scarce area. By adopting vertical farming technologies, Singapore has been able to overcome limitations posed by land scarcity and water constraints. Since this shift in agriculture, the authors note that Singapore has reduced their dependence on food imports and enhanced their resilience to external disruptions. The case study underscores the adaptability of vertical farming solutions, demonstrating their applicability in diverse urban settings facing similar challenges reinforcing the importance of embracing innovative approaches like vertical farming to build resilient food systems capable of meeting the evolving needs of urban populations in an increasingly uncertain world.

This is a vertical farm in an indoor environment, showcasing the space efficiency and abundance of produce in a dense area.
Vertical farming maximizes space efficiency and minimizes resource consumption which is the exact fight we are facing with current agricultural practices. Unlike traditional farming, which sprawls across a large portion of arable land, consuming significant quantities of water, vertical farms stack crops in controlled indoor environments. This not only addresses the issue of land scarcity but also addresses the environmental footprint associated with traditional farming practices. Issues such as pesticide contamination, soil degradation, and habitat destruction are significantly reduced through controlled growing conditions that eliminate the need for chemical inputs.
Synthesis and Conclusion
The conversation surrounding vertical farming incorporates diverse perspectives that each contribute to a better understanding of its potential in our agricultural system. Scholarly research sheds light on the environmental benefits of vertical farming, emphasizing its potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, optimize resource usage, and mitigate the negative impacts of conventional agriculture on land, water, and biodiversity. Hundreds of studies provide evidence of the feasibility and sustainable vertical farming systems, demonstrating their capacity to increase food production in urban areas while minimizing environmental degradation. Similarly, insights from industry leaders highlight the crucial role of collaboration and innovation in advancing vertical farming practices. Their advocacy for closer integration between vertical farms and traditional agriculture underscores the importance of shared goals and mutual support to tackle common challenges. By facilitating partnerships and knowledge exchange among stakeholders, the industry can accelerate the adoption and scalability of vertical farming, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient food system.
Vertical farming signifies a revolutionary shift in agricultural approaches, providing innovative solutions to address urgent global challenges such as food insecurity, environmental degradation, and urbanization. Through collaboration, leveraging technologies, and embracing sustainable urban planning, vertical farming holds the promise of revolutionizing food production systems and enhancing resilience in the face of environmental and societal pressures. In our current increasingly interconnected world, vertical farming emerges as a beacon of hope, offering a pathway towards a more sustainable and equitable future for generations to come and as cities continue to expand and populations grow. Moreover, vertical farming offers a promising pathway towards sustainable urban agriculture, resilience, and food security in an our always changing uncertain world.

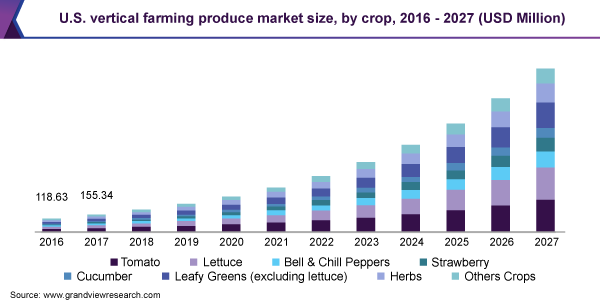

No comments yet.